Web Hosting: A Simple Guide to Choosing the Right Provider

 Written by Massa Medi| January 2, 2025
Written by Massa Medi| January 2, 2025
Web hosting is like renting a space for your website so that people can find and visit it online. This guide will help you understand the different types of web hosting available, give you examples of good providers, and share tips to help you make the best choice. We’ll also point out some common mistakes to avoid when choosing a hosting service.
Different Types of Web Hosting
1. Shared Hosting
Shared hosting is perfect for small websites or blogs that don’t get too much traffic. It means your website will share a server (a powerful computer that stores your website) with other websites. Think of it like sharing an apartment with roommates. Some popular shared hosting providers are Bluehost, HostGator, and GoDaddy.
Pros: It's affordable, easy to set up, and great for beginners.
Cons: Your website might load slower if other websites on the same server have a lot of visitors, and there could be higher security risks.
2. Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting
VPS hosting gives you a dedicated portion of a server, like having your own room in an apartment building. This means better performance and more control. Good VPS providers include Digital Ocean, Linode, and InMotion Hosting.
Pros: More security and customization. Good for websites with moderate to high traffic.
Cons: It can be more expensive and may require some technical know-how.
3. Dedicated Hosting
Dedicated hosting is like renting an entire house for yourself. You get a whole server just for your website, which means maximum performance and security. Examples of dedicated hosting providers are Liquid Web, Hostwinds, and 1&1 IONOS.
Pros: Fast load times and stability since no one else is using your server.
Cons: It's much pricier and needs a higher level of technical skill to manage.
4. Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting spreads your website across multiple servers, which is like having your files saved in several places. This makes your site more flexible and scalable. Some cloud hosting providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
Pros: Great for handling lots of visitors and very reliable.
Cons: It can be tricky to set up, and costs can vary.
5. Managed Hosting
With managed hosting, the provider takes care of all the technical stuff for you. They set up, maintain, and secure the server. Providers like WP Engine, Flywheel, and Kinsta offer managed hosting.
Pros: Saves you time and ensures your website runs smoothly.
Cons: It can be more expensive and may offer less flexibility in customization.
6. Colocation Hosting
Colocation hosting means you have your own server but rent space in a data center to store it. This is for those who want full control over their server hardware. Providers like Equinix, CyrusOne, and Digital Realty offer this service.
Pros: You have complete control and a highly secure environment.
Cons: You’ll need to buy your own hardware and have advanced technical skills.
Avoiding Scams and Choosing the Right Provider
It’s important to be careful when choosing a web hosting provider. Here are some simple tips to help you avoid scams:
- Research and Reviews: Look up reviews from trustworthy sources about the provider you’re considering. Check how they handle uptime (how often their servers are running) and how they support their customers.
- Understand Pricing: Be careful with very low prices or hidden fees. Compare what different plans offer to get the best deal for your needs.
- Security and Privacy: Make sure the provider has good security features like SSL certificates (which protect your website) and regular updates.
- Support and Documentation: Choose providers with helpful customer support. Good documentation and tutorials can also help you manage your hosting account.
- Contract Terms: Read the fine print in the contract to understand cancellation policies, refund policies, and any limits on how much you can use the resources.
Free Hosting Options: GitHub, Netlify, and Vercel
If you’re just starting or working on a small project, free hosting options like GitHub Pages, Netlify, and Vercel are great choices. Here’s a quick look at each:
- GitHub Pages: This service allows you to host static websites for free. Just create a repository on GitHub, upload your website files, and enable GitHub Pages to publish your site.
Check out this video on how to upload your website on GitHub
- Netlify: Netlify makes it easy to deploy and host static sites with features like automatic updates and serverless functions. Connect it to your GitHub repository, and your site updates automatically with each change.
Watch this video on how to upload your website on Netlify
- Vercel: Vercel is great for hosting static sites and React applications. It provides features like automatic scaling and serverless functions. Just connect it to your GitHub repository, and your site will deploy smoothly.
Check out this video on how to Deploy Your website on Vercel through GitHub
Steps to Host Your Website: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and React
Here are the steps to host a website that includes HTML, CSS, and JavaScript:
- Choose a Hosting Provider: Pick a provider that suits your needs based on your research. Look for features like uptime guarantees (the promise that your website will be available), scalability (the ability to grow with your traffic), and customer support.
- Purchase a Hosting Plan: Review the hosting plans they offer and select one that fits your website's needs, considering expected traffic and storage requirements.
- Upload Your Files: After purchasing, you'll get access details. Use an FTP (File Transfer Protocol) client to connect to your server and upload your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files to the right folder.
- Configure Your Server: Depending on your site’s needs, you may need to adjust server settings, like setting up a database or enabling security features.
- Test and Publish: Before your site goes live, check everything works properly. Once you’re happy, point your domain to your server and make your site accessible to everyone.
Conclusion
Choosing the right web hosting service is crucial for your website's success. Consider your needs, do your research, and choose wisely to ensure a smooth and effective online presence.
Recommended
Explore More Recent Blog Posts

Understanding How the Internet Works
January 13, 2025
Learn how the internet functions, from the basics of networking to protocols like HTTP. Understand key concepts like IP addresses, DNS, and data packet routing.

Progressive Web Apps: A Step-by-Step Guide
January 14, 2025
Learn the essentials of building Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) that combine the best of web and mobile apps. This guide covers service workers, manifest files, and offline capabilities to create a seamless user experience.

Mastering SEO and Content Marketing Strategies
January 10, 2025
Unlock the secrets of search engine optimization (SEO) and content marketing. Understand how Google indexes pages and learn to create valuable content that attracts and engages your target audience.

Web Analytics: Tracking User Behavior for Better UX
January 8, 2025
Harness the power of web analytics to improve your website's user experience. Learn how to set up Google Analytics, interpret user behavior data, and use tools like Hotjar and Crazy Egg to optimize your site's performance and conversion rates.

Cybersecurity Essentials for Web Developers
January 4, 2025
Protect your website and users with essential cybersecurity practices. Explore the importance of HTTPS, SSL certificates, and learn about common vulnerabilities like XSS and CSRF.

Monetization Strategies for Tech Professionals
January 1, 2025
Explore various ways to monetize your tech skills. From freelancing on platforms like Upwork and Fiverr to creating and selling digital products.

AI Tools for Developers: Boosting Productivity and Creativity
January 12, 2025
Leverage the power of AI to enhance your development workflow. Discover how tools like ChatGPT and GitHub Copilot can assist in coding, content creation, and problem-solving.

The Rise of No-Code and Low-Code Platforms
January 14, 2025
Explore the growing trend of no-code and low-code platforms. Understand how these tools are changing the landscape of web development and enabling non-technical users to create sophisticated applications.

Blockchain and Web3: The Future of the Internet
January 3, 2025
Dive into the world of blockchain technology and Web3. Understand the fundamentals of decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and cryptocurrencies.

Why Learn React in 2025?
January 13, 2025
Explore the reasons behind React's enduring popularity in 2024. Learn about its efficiency, component-based architecture, and the vibrant ecosystem of libraries that support modern web development.

Understanding JavaScript Closures
January 6, 2025
Dive deep into the concept of closures in JavaScript. Learn how closures work, why they are useful, and how they can help you manage scope and data encapsulation in your applications.
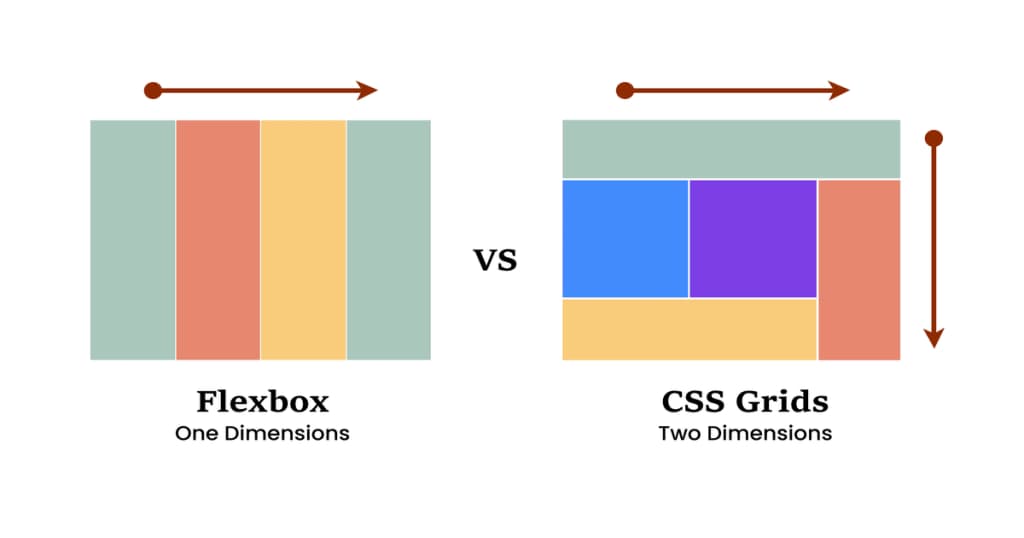
CSS Grid vs. Flexbox: Which to Choose?
January 2, 2025
Understand the differences between CSS Grid and Flexbox, two powerful layout systems in modern web design. This post will help you decide which tool to use based on your project's needs.

React Hooks: A Comprehensive Guide
January 7, 2025
Get a thorough understanding of React Hooks and how they revolutionize state management in functional components. Explore hooks like useState, useEffect, and custom hooks.

The Ultimate Guide to Google Search Console in 2024
January 7, 2025
Navigate the features and functionalities of Google Search Console to enhance your website's SEO performance. This guide covers setting up your account and using insights to improve your content strategy.

Domain Names: What They Are and How to Choose One
January 12, 2025
Learn about domain names, their structure, and the importance of choosing the right one for your online presence. This post covers best practices for selecting domain names that enhance branding and SEO.

Online Courses and Starting a Tech YouTube Channel: Sharing Your Knowledge and Impacting Lives
January 1, 2025
Learn how to create and sell online courses to share your expertise, and explore the steps to start a tech YouTube channel that can reach and engage a global audience. This blog covers the benefits of online courses, planning content, and strategies to grow a successful YouTube channel.
Unleashing the Power of SSL Certificates: Why SSL Matters for Your Website
January 10, 2025
Learn about SSL certificates and their importance in protecting websites. Understand data encryption, authentication, and the types of SSL certificates available, including Domain Validation, Organization Validation, and Extended Validation SSL. Discover how SSL boosts user trust and search engine rankings while ensuring legal compliance.

The Importance of Version Control in Software Development
January 9, 2025
Explore the critical role of version control systems like Git in software development. Understand how version control helps manage changes, collaborate with teams, and maintain project history.

Building Networks as Developers: A Comprehensive Guide to Professional Connections
January 4, 2025
Learn how to build a strong network as a developer and maximize your online presence.

The Internet of Things (IoT): Revolutionizing Our Connected World
January 5, 2025
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming the way we live and work by connecting everyday devices to the internet, allowing them to exchange data. This article explores IoT, its history, architecture, real-world applications, and its future impact on industries like healthcare, agriculture, and smart cities. It also discusses the role of AI in IoT, security challenges, and ethical implications.