Cybersecurity Essentials for Web Developers: Safeguarding Your Digital Fortress

 Written by Massa Medi| January 4, 2025
Written by Massa Medi| January 4, 2025
In an era where digital presence is paramount, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. As web developers, we're not just builders of digital experiences; we're the first line of defense against an ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to fortify your web applications, protect user data, and maintain the integrity of your digital creations.
Whether you're a seasoned developer looking to reinforce your security practices or a newcomer eager to build with a security-first mindset, this deep dive into cybersecurity essentials will empower you to create safer, more resilient web applications. Let's embark on this crucial journey to transform your development approach and safeguard the digital world we're building together.
Understanding the Cybersecurity Landscape
Before we delve into specific security measures, it's crucial to understand the current cybersecurity landscape and the threats we face as web developers:
Common Web Application Vulnerabilities
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users.
- SQL Injection: Enables attackers to interfere with database queries, potentially accessing or manipulating sensitive data.
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF): Tricks users into performing unintended actions on a web application they're authenticated to.
- Broken Authentication: Weaknesses in authentication mechanisms that can lead to unauthorized access.
- Sensitive Data Exposure: Inadequate protection of sensitive user data, both in transit and at rest.
- XML External Entities (XXE): Vulnerabilities in XML processing that can lead to data disclosure or denial of service.
- Broken Access Control: Failures in enforcing proper access restrictions on resources.
Emerging Threats
As technology evolves, so do the threats we face. Some emerging concerns include:
- API Vulnerabilities: As applications become more interconnected, securing APIs becomes crucial.
- Serverless Security: The rise of serverless architectures introduces new security challenges.
- AI-Powered Attacks: Cybercriminals are leveraging AI to create more sophisticated and targeted attacks.
- IoT Vulnerabilities: The growing Internet of Things ecosystem expands the attack surface for web applications.
Essential Security Measures for Web Developers
Now that we understand the threats, let's explore the fundamental security measures every web developer should implement:
1. Implement HTTPS Everywhere
HTTPS is no longer optional; it's a necessity. Here's why and how to implement it:
- Why it matters: HTTPS encrypts data in transit, protecting it from eavesdropping and tampering.
- Implementation:
- Obtain an SSL/TLS certificate (Consider free options like Let's Encrypt).
- Configure your web server to use HTTPS.
- Implement HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) headers.
- Redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS.
- Best practices:
- Use strong cipher suites and disable outdated protocols.
- Regularly renew and update your SSL/TLS certificates.
- Consider implementing Certificate Transparency (CT) logging.
2. Input Validation and Sanitization
Never trust user input. Proper validation and sanitization are crucial for preventing a wide range of attacks:
- Client-side validation: Implement for user experience, but never rely on it for security.
- Server-side validation: Always validate and sanitize input on the server.
- Techniques:
- Use whitelisting to allow only known-good input.
- Implement strict type checking.
- Encode output to prevent XSS attacks.
- Use parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection.
3. Secure Authentication and Session Management
Robust authentication is your first line of defense against unauthorized access:
- Password security:
- Enforce strong password policies (length, complexity).
- Use secure password hashing algorithms (e.g., bcrypt, Argon2).
- Implement account lockout policies to prevent brute-force attacks.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an extra layer of security.
- Session management:
- Use secure, HttpOnly, and SameSite cookies for session tokens.
- Implement proper session timeout and renewal mechanisms.
- Securely handle session termination (logout functionality).
4. Implement Proper Access Controls
Ensure users can only access resources they're authorized to:
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Define and enforce user roles and permissions.
- Principle of least privilege: Grant users the minimum level of access necessary.
- API security: Implement proper authentication and authorization for all API endpoints.
5. Secure Data Storage and Transmission
Protect sensitive data both at rest and in transit:
- Data encryption: Use strong encryption algorithms for sensitive data storage.
- Key management: Implement secure key storage and rotation practices.
- Data minimization: Only collect and retain necessary data.
- Secure backups: Regularly backup data and ensure backups are encrypted and securely stored.
6. Implement Security Headers
HTTP security headers add an extra layer of protection against various attacks:
- Content Security Policy (CSP): Mitigate XSS and other injection attacks.
- X-Frame-Options: Prevent clickjacking attacks.
- X-XSS-Protection: Enable browser's built-in XSS protection (for older browsers).
- Referrer-Policy: Control how much referrer information is included with requests.
7. Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Proactively identify and address vulnerabilities:
- Automated scanning: Use tools like OWASP ZAP or Burp Suite for regular vulnerability scans.
- Manual code reviews: Conduct peer reviews with a focus on security.
- Penetration testing: Engage professional penetration testers to simulate real-world attacks.
Advanced Security Techniques
For those looking to take their security practices to the next level, consider these advanced techniques:
1. Implement a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A WAF can provide an additional layer of protection against common web attacks:
- Choose between cloud-based WAFs (e.g., Cloudflare, AWS WAF) or self-hosted solutions (e.g., ModSecurity).
- Regularly update and tune WAF rules to balance security and functionality.
2. Utilize Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP)
RASP technology integrates with your application to detect and prevent real-time attacks:
- Implement RASP solutions to provide context-aware security.
- Use RASP in conjunction with other security measures for a defense-in-depth approach.
3. Adopt a DevSecOps Approach
Integrate security into your development lifecycle:
- Implement security checks in your CI/CD pipeline.
- Use tools like SAST (Static Application Security Testing) and DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing).
- Foster a security-aware culture within your development team.
4. Implement Secure Coding Practices
Adopt a secure-by-design approach to development:
- Follow secure coding guidelines specific to your programming language and framework.
- Use security-focused code linters and static analysis tools.
- Regularly update and patch all dependencies and libraries.
Handling Security Incidents
Despite our best efforts, security incidents can still occur. Being prepared is crucial:
1. Develop an Incident Response Plan
- Define roles and responsibilities for incident response.
- Establish clear communication channels and escalation procedures.
- Regularly practice and update your incident response plan.
2. Implement Logging and Monitoring
- Set up comprehensive logging for all security-relevant events.
- Implement real-time alerting for suspicious activities.
- Regularly review and analyze logs for potential security issues.
3. Have a Data Breach Response Strategy
- Understand your legal obligations for data breach notifications.
- Prepare templates for communication with affected users and stakeholders.
- Have a plan for post-incident analysis and implementing lessons learned.
Staying Informed and Continuous Learning
The field of cybersecurity is constantly evolving. To stay ahead, consider these practices:
- Follow reputable security blogs and news sources (e.g., OWASP, US-CERT, Krebs on Security).
- Participate in security-focused webinars and conferences.
- Consider obtaining relevant security certifications (e.g., CISSP, CEH).
- Engage with the security community through forums and social media.
Conclusion: Building a Secure Digital Future
As web developers, we hold a significant responsibility in shaping a secure digital landscape. By implementing these cybersecurity essentials, staying vigilant, and continuously updating our knowledge and skills, we can create web applications that not only provide great user experiences but also stand resilient against the evolving threats in the digital world.
Remember, security is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Embrace a security-first mindset in all your development efforts, and you'll be contributing to a safer, more trustworthy internet for everyone. Stay curious, stay vigilant, and keep building secure digital experiences!
Recommended
Explore More Recent Blog Posts

Understanding How the Internet Works
January 13, 2025
Learn how the internet functions, from the basics of networking to protocols like HTTP. Understand key concepts like IP addresses, DNS, and data packet routing.

Progressive Web Apps: A Step-by-Step Guide
January 14, 2025
Learn the essentials of building Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) that combine the best of web and mobile apps. This guide covers service workers, manifest files, and offline capabilities to create a seamless user experience.

Mastering SEO and Content Marketing Strategies
January 10, 2025
Unlock the secrets of search engine optimization (SEO) and content marketing. Understand how Google indexes pages and learn to create valuable content that attracts and engages your target audience.

Web Analytics: Tracking User Behavior for Better UX
January 8, 2025
Harness the power of web analytics to improve your website's user experience. Learn how to set up Google Analytics, interpret user behavior data, and use tools like Hotjar and Crazy Egg to optimize your site's performance and conversion rates.

Monetization Strategies for Tech Professionals
January 1, 2025
Explore various ways to monetize your tech skills. From freelancing on platforms like Upwork and Fiverr to creating and selling digital products.

AI Tools for Developers: Boosting Productivity and Creativity
January 12, 2025
Leverage the power of AI to enhance your development workflow. Discover how tools like ChatGPT and GitHub Copilot can assist in coding, content creation, and problem-solving.

The Rise of No-Code and Low-Code Platforms
January 14, 2025
Explore the growing trend of no-code and low-code platforms. Understand how these tools are changing the landscape of web development and enabling non-technical users to create sophisticated applications.

Blockchain and Web3: The Future of the Internet
January 3, 2025
Dive into the world of blockchain technology and Web3. Understand the fundamentals of decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and cryptocurrencies.

Why Learn React in 2025?
January 13, 2025
Explore the reasons behind React's enduring popularity in 2024. Learn about its efficiency, component-based architecture, and the vibrant ecosystem of libraries that support modern web development.

Understanding JavaScript Closures
January 6, 2025
Dive deep into the concept of closures in JavaScript. Learn how closures work, why they are useful, and how they can help you manage scope and data encapsulation in your applications.
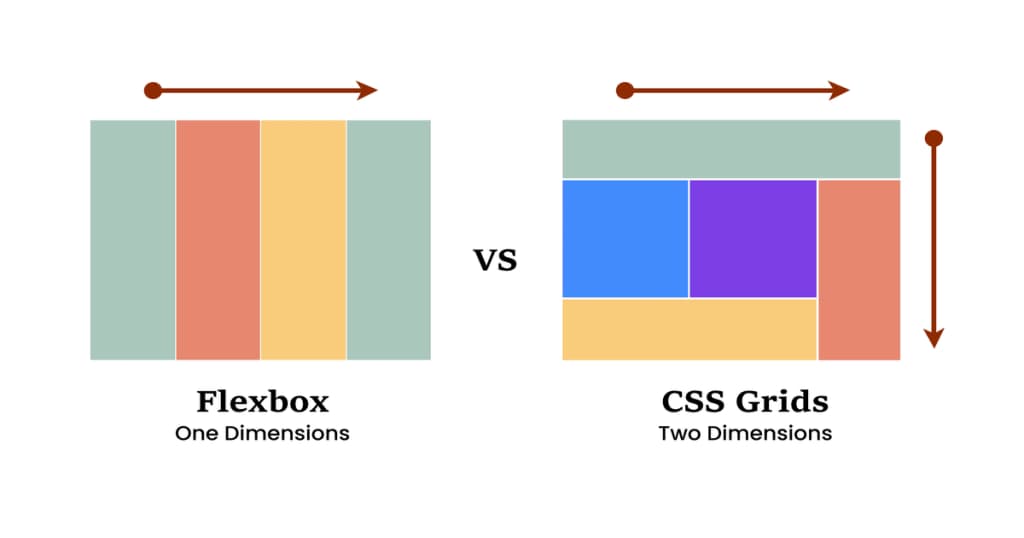
CSS Grid vs. Flexbox: Which to Choose?
January 2, 2025
Understand the differences between CSS Grid and Flexbox, two powerful layout systems in modern web design. This post will help you decide which tool to use based on your project's needs.

React Hooks: A Comprehensive Guide
January 7, 2025
Get a thorough understanding of React Hooks and how they revolutionize state management in functional components. Explore hooks like useState, useEffect, and custom hooks.

The Ultimate Guide to Google Search Console in 2024
January 7, 2025
Navigate the features and functionalities of Google Search Console to enhance your website's SEO performance. This guide covers setting up your account and using insights to improve your content strategy.

Domain Names: What They Are and How to Choose One
January 12, 2025
Learn about domain names, their structure, and the importance of choosing the right one for your online presence. This post covers best practices for selecting domain names that enhance branding and SEO.

Web Hosting: A Simple Guide to Choosing the Right Provider
January 2, 2025
This guide provides an overview of different types of web hosting services, including shared, VPS, dedicated, cloud, managed, and colocation hosting. It offers practical examples of providers, tips for avoiding scams, and guidance on choosing the right service for your needs. Additionally, it highlights free hosting options like GitHub Pages, Netlify, and Vercel, along with steps for hosting a website that uses HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.

Online Courses and Starting a Tech YouTube Channel: Sharing Your Knowledge and Impacting Lives
January 1, 2025
Learn how to create and sell online courses to share your expertise, and explore the steps to start a tech YouTube channel that can reach and engage a global audience. This blog covers the benefits of online courses, planning content, and strategies to grow a successful YouTube channel.
Unleashing the Power of SSL Certificates: Why SSL Matters for Your Website
January 10, 2025
Learn about SSL certificates and their importance in protecting websites. Understand data encryption, authentication, and the types of SSL certificates available, including Domain Validation, Organization Validation, and Extended Validation SSL. Discover how SSL boosts user trust and search engine rankings while ensuring legal compliance.

The Importance of Version Control in Software Development
January 9, 2025
Explore the critical role of version control systems like Git in software development. Understand how version control helps manage changes, collaborate with teams, and maintain project history.

Building Networks as Developers: A Comprehensive Guide to Professional Connections
January 4, 2025
Learn how to build a strong network as a developer and maximize your online presence.

The Internet of Things (IoT): Revolutionizing Our Connected World
January 5, 2025
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming the way we live and work by connecting everyday devices to the internet, allowing them to exchange data. This article explores IoT, its history, architecture, real-world applications, and its future impact on industries like healthcare, agriculture, and smart cities. It also discusses the role of AI in IoT, security challenges, and ethical implications.