The Internet of Things (IoT): Revolutionizing Our Connected World

 Written by Massa Medi| January 5, 2025
Written by Massa Medi| January 5, 2025
The Internet of Things (IoT) has become one of the most important innovations in recent times, reshaping industries, homes, and cities. By connecting devices and enabling them to exchange data, IoT is creating a smarter and more interconnected world. From smart refrigerators to industrial machinery, IoT impacts how we live, work, and interact with the world around us.
But what exactly is IoT, how does it work, and what are the potential implications for the future?
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices—like cars, home appliances, wearable gadgets, and industrial equipment—connected to the internet, enabling them to collect and share data. These devices can communicate with each other, making it easier to monitor, control, and automate processes.
Historical Development of IoT
While IoT is booming now, its origins trace back to the early 1980s. The first internet-connected device was a Coke vending machine at Carnegie Mellon University, which allowed programmers to check the availability of cold drinks. However, the true rise of IoT began in the early 2000s, with advances in wireless communication, sensors, and cloud computing. The term “Internet of Things” was coined by Kevin Ashton in 1999, and since then, the growth has been exponential, with IoT transforming industries worldwide.
How IoT Works: IoT Architecture
IoT systems rely on a three-layered architecture: perception, network, and application.
- Perception Layer: This is the layer where data is gathered through sensors or actuators. It includes devices like temperature sensors, RFID tags, or motion detectors that sense environmental factors.
- Network Layer: After the data is collected, it is transmitted over the network layer, which could be wireless (Wi-Fi, cellular networks) or wired (Ethernet).
- Application Layer: Once the data is transmitted, it is processed and analyzed in the application layer. This is where data is used to make decisions, provide insights, or trigger actions. For example, in a smart home system, data from motion sensors could trigger lighting to turn on automatically when you enter a room.
Use Cases of IoT
The applications of IoT are vast, impacting a wide range of sectors. Let’s explore some real-world examples:
- Smart Homes: Devices like Amazon Echo, Google Nest, and smart thermostats are bringing IoT into our everyday lives by automating tasks like controlling home appliances, lighting, and security systems.
- Healthcare: Wearable IoT devices like Fitbit or heart monitors can track patient data in real-time, providing healthcare providers with essential information to manage chronic conditions or detect emergencies.
- Agriculture: IoT is transforming agriculture with smart farming techniques. Sensors in fields monitor soil conditions, and weather data can automatically adjust irrigation, ensuring optimal crop growth while conserving water.
- Manufacturing: IoT devices are revolutionizing industries with predictive maintenance. By collecting data from machines, manufacturers can detect signs of malfunction before they occur, reducing downtime and costs.
Future of IoT: 5G and Beyond
The future of IoT is closely tied to the deployment of 5G technology. With its high speeds and low latency, 5G enables a massive expansion of IoT, especially in industries like autonomous vehicles and smart cities. For example, in a smart city, 5G will allow thousands of devices to communicate in real-time—everything from traffic lights to security cameras—making cities more efficient, safer, and responsive.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in IoT
Another significant advancement in IoT is its integration with AI and machine learning (ML). AI can analyze the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices, providing valuable insights and even predicting trends. This integration leads to smarter systems that can automate complex processes.
For example, in healthcare, AI-enabled IoT devices can monitor patients’ vitals and use machine learning algorithms to predict health issues before they become critical, allowing doctors to intervene early.
Security Challenges in IoT
As more devices connect to the internet, the risk of security breaches grows. The 2016 Mirai botnet attack, where hackers exploited vulnerable IoT devices to disrupt major websites like Twitter and Netflix, showed how unsecured IoT systems could be manipulated. Addressing security concerns is crucial for the future of IoT.
Solutions such as end-to-end encryption, secure device authentication, and the use of blockchain technology for tamper-proof transactions are being explored to safeguard IoT networks.
The Ethical Implications of IoT
While IoT brings convenience and efficiency, it also raises important ethical questions. The collection of personal data by IoT devices could lead to privacy violations if not properly regulated. Additionally, the increased automation could displace jobs in certain sectors, requiring a societal discussion on how to manage these impacts responsibly.
Case Study: Walmart’s Use of IoT in Supply Chain Management
Walmart has been a pioneer in using IoT to optimize its supply chain. By tracking inventory levels in real-time, Walmart can ensure that its stores are always well-stocked. IoT-enabled sensors in warehouses monitor everything from temperature to stock levels, helping the company maintain efficiency while reducing waste.
In the agricultural sector, companies like John Deere are also using IoT to revolutionize farming. Their IoT-enabled equipment collects data from the fields to help farmers optimize irrigation and fertilizer usage, ensuring better crop yields and sustainability.
Emerging Technologies in IoT: Edge Computing and Quantum Computing
Edge computing is becoming increasingly important in the IoT ecosystem. Instead of sending all the data to a centralized cloud for processing, edge computing allows data to be processed closer to where it is generated. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage, making IoT systems faster and more efficient.
Quantum computing, still in its early stages, promises to take IoT to the next level by solving complex problems in real-time, such as optimizing traffic flow in smart cities.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things is revolutionizing the way we live and work. From smart homes to industrial applications, IoT is making the world more connected, efficient, and data-driven. As we move into the future, with the rise of 5G, AI, and other emerging technologies, IoT will continue to play an integral role in shaping our connected world.
However, it’s essential to address the security and ethical implications that come with this growth. By doing so, we can ensure that IoT delivers on its potential while safeguarding privacy and promoting responsible innovation.
Recommended
Explore More Recent Blog Posts

Understanding How the Internet Works
January 13, 2025
Learn how the internet functions, from the basics of networking to protocols like HTTP. Understand key concepts like IP addresses, DNS, and data packet routing.

Progressive Web Apps: A Step-by-Step Guide
January 14, 2025
Learn the essentials of building Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) that combine the best of web and mobile apps. This guide covers service workers, manifest files, and offline capabilities to create a seamless user experience.

Mastering SEO and Content Marketing Strategies
January 10, 2025
Unlock the secrets of search engine optimization (SEO) and content marketing. Understand how Google indexes pages and learn to create valuable content that attracts and engages your target audience.

Web Analytics: Tracking User Behavior for Better UX
January 8, 2025
Harness the power of web analytics to improve your website's user experience. Learn how to set up Google Analytics, interpret user behavior data, and use tools like Hotjar and Crazy Egg to optimize your site's performance and conversion rates.

Cybersecurity Essentials for Web Developers
January 4, 2025
Protect your website and users with essential cybersecurity practices. Explore the importance of HTTPS, SSL certificates, and learn about common vulnerabilities like XSS and CSRF.

Monetization Strategies for Tech Professionals
January 1, 2025
Explore various ways to monetize your tech skills. From freelancing on platforms like Upwork and Fiverr to creating and selling digital products.

AI Tools for Developers: Boosting Productivity and Creativity
January 12, 2025
Leverage the power of AI to enhance your development workflow. Discover how tools like ChatGPT and GitHub Copilot can assist in coding, content creation, and problem-solving.

The Rise of No-Code and Low-Code Platforms
January 14, 2025
Explore the growing trend of no-code and low-code platforms. Understand how these tools are changing the landscape of web development and enabling non-technical users to create sophisticated applications.

Blockchain and Web3: The Future of the Internet
January 3, 2025
Dive into the world of blockchain technology and Web3. Understand the fundamentals of decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and cryptocurrencies.

Why Learn React in 2025?
January 13, 2025
Explore the reasons behind React's enduring popularity in 2024. Learn about its efficiency, component-based architecture, and the vibrant ecosystem of libraries that support modern web development.

Understanding JavaScript Closures
January 6, 2025
Dive deep into the concept of closures in JavaScript. Learn how closures work, why they are useful, and how they can help you manage scope and data encapsulation in your applications.
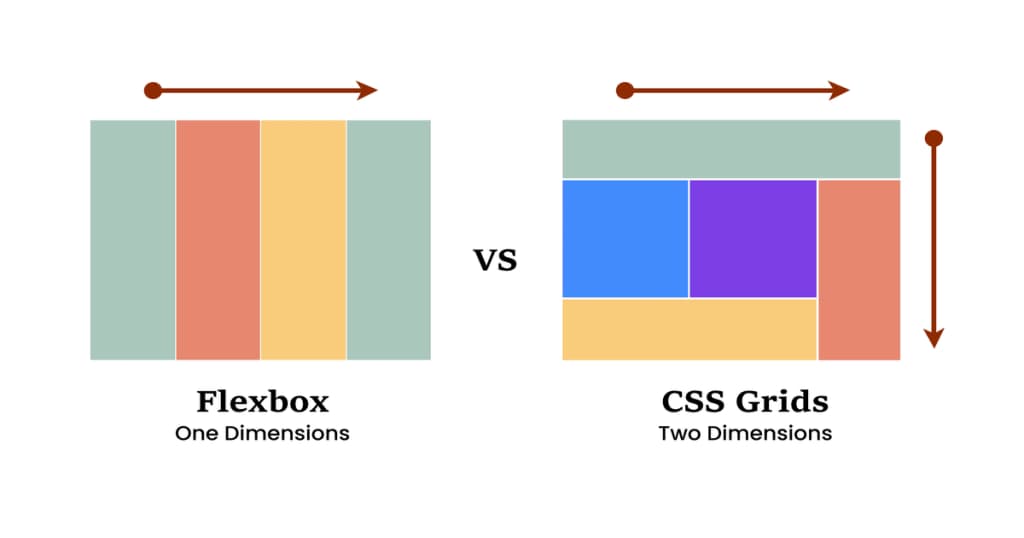
CSS Grid vs. Flexbox: Which to Choose?
January 2, 2025
Understand the differences between CSS Grid and Flexbox, two powerful layout systems in modern web design. This post will help you decide which tool to use based on your project's needs.

React Hooks: A Comprehensive Guide
January 7, 2025
Get a thorough understanding of React Hooks and how they revolutionize state management in functional components. Explore hooks like useState, useEffect, and custom hooks.

The Ultimate Guide to Google Search Console in 2024
January 7, 2025
Navigate the features and functionalities of Google Search Console to enhance your website's SEO performance. This guide covers setting up your account and using insights to improve your content strategy.

Domain Names: What They Are and How to Choose One
January 12, 2025
Learn about domain names, their structure, and the importance of choosing the right one for your online presence. This post covers best practices for selecting domain names that enhance branding and SEO.

Web Hosting: A Simple Guide to Choosing the Right Provider
January 2, 2025
This guide provides an overview of different types of web hosting services, including shared, VPS, dedicated, cloud, managed, and colocation hosting. It offers practical examples of providers, tips for avoiding scams, and guidance on choosing the right service for your needs. Additionally, it highlights free hosting options like GitHub Pages, Netlify, and Vercel, along with steps for hosting a website that uses HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.

Online Courses and Starting a Tech YouTube Channel: Sharing Your Knowledge and Impacting Lives
January 1, 2025
Learn how to create and sell online courses to share your expertise, and explore the steps to start a tech YouTube channel that can reach and engage a global audience. This blog covers the benefits of online courses, planning content, and strategies to grow a successful YouTube channel.
Unleashing the Power of SSL Certificates: Why SSL Matters for Your Website
January 10, 2025
Learn about SSL certificates and their importance in protecting websites. Understand data encryption, authentication, and the types of SSL certificates available, including Domain Validation, Organization Validation, and Extended Validation SSL. Discover how SSL boosts user trust and search engine rankings while ensuring legal compliance.

The Importance of Version Control in Software Development
January 9, 2025
Explore the critical role of version control systems like Git in software development. Understand how version control helps manage changes, collaborate with teams, and maintain project history.

Building Networks as Developers: A Comprehensive Guide to Professional Connections
January 4, 2025
Learn how to build a strong network as a developer and maximize your online presence.